What is Shoulder Bursitis?
Let us first answer the question – What is a bursa? A bursa is a little sac of fluid that is usually present adjacent to fat pads. Shoulder bursitis is the inflammation of bursae in the shoulder jointThe glenohumeral joint is a ball-and-socket synovial joint and is the most mobile joint in the human More.
The bursae usually exist in areas of potential stress. Their function is to help absorb force and protect the connective tissues present around the joint. The figure below shows the bursae surrounding the shoulder complex.
1. Subacromial-subdeltoid bursa (SASD)
2. Subscapular recess
3. Sub-coracoid bursa
4. Coracoclavicular bursa
5. Supra-acromial bursa
6. Medial extension of the SASD bursa
Due to repetitive compression between two bones, the bursa may get irritated and as a result, get inflamed. This inflammation of the bursa is termed bursitis.
The main shoulder bursa leading to bursitis is the SASD bursa. its primary function is to reduce friction allowing internal rotation of the humerus under the acromion during shoulder movements.
Shoulder Bursitis Causes
The causes of bursitis are as follows:
1. Trauma – either due to a single blow or repetitive trauma
2. Infection – acute or chronic
3. Metabolic diseases (e.g., Gout)
4. Inflammatory disorders (e.g., Rheumatoid arthritis)
5. Unaccustomed activity (e.g., exercises, ill-fitting shoes)
6. Due to excessive pressure (e.g., friction)
The name bursitis itself is often a misnomer, as not all forms of bursitis are due to a primary inflammatory process but are rather a swelling of the bursa due to a noxious stimulus.
What are the symptoms of shoulder bursitis?
The symptoms of shoulder bursitis depend on its cause and severity.
Patients with acute bursitis typically experience pain when the bursa is palpated (=tenderness). Due to discomfort, the range of motion of the affected joint may be reduced. Active motion involving the injured bursa also causes discomfort, however, the position of the bursa and the biomechanics of moving the surrounding bones, muscles, and tissues will determine these factors.
Many patients will experience pain while actively moving their arm, but any passive motion (when somebody else takes the weight of your arm and moves it for you) may alleviate it. This may be because the muscles surrounding the bursa are inactive and thus, don’t compress it causing little to no pain.
Chronic bursitis, on the other hand, has unresolved swelling; it is very rarely accompanied by pain and redness.
What is the treatment for shoulder bursitis?
Reduce Inflammation
Reduction of the underlying inflammation is the primary step while treating shoulder bursitis. NSAIDs (Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs) are the first line of treatment. These drugs help in reducing the swelling and also help with the pain. Medications and rest are usually sufficient.
Hydrocortisone Injections
Should the symptoms prevail, hydrocortisone injections are the next choice of treatment. However, cortisone is a steroid hormone and should be discussed with the doctor thoroughly, especially when taking repeat injections.
Bursae are meant to undergo forces and compression. However, if you do end up with bursitis, it means the force acting upon the bursa is excessive and imbalanced. This is when exercises come into the picture. To prevent recurrent episodes of bursitis, strengthening the shoulder and scapular muscles is very important.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy and range of motion exercises play a role in supporting the area around the bursa. This is particularly important in subacromial bursitis, where immobilization may result in complications like atrophy (muscle wasting), retraction, and a frozen shoulderA condition where shoulder movement becomes very limited and painful. The cause is often unknown, bu More.
In the acute state, pain may be disabling and can be treated with pain-relieving modalities (Cryotherapy, TENS, Ultrasound, etc). Gentle mobility exercises carried out judiciously not only induce relaxation but also bring about improvement in muscle capillary filling.
The patient should avoid repeated frictional movements (e.g shoulder abductionIs a sideways upgoing movement in the frontal plane brought about by the supraspinatus and the mid More in subdeltoid bursitis). Exercises should be progressed to active and then resisted gradually, depending on patients’ pain and symptoms.
Re-education is usually started in the supine (sleeping) position to ensure your shoulder is passively supported. As the patient can actively start supporting their shoulder, exercises are progressed to the challenging ‘against gravity’ plane.
In bursitis caused by systemic inflammatory conditions, it is important that the physician treats the underlying condition.
What is the surgical treatment for shoulder bursitis?
Only in patients that are unresponsive to conservative treatment, will the surgical treatment be chosen.
A bursectomy (removal of the bursa) may be performed arthroscopically (done using a small incision with a special, minimally invasive probe called an arthroscope).
An open approach may be chosen if the cause of bursitis is accompanied by the need to carry out a subacromial decompression (it is a surgery done to increase the size of the subacromial space by trimming the bones around it and thus, reducing any pressure on the tendons and bursa), rotator cuffThe rotator cuff is a group of muscles and tendons that attach the shoulder blade to the upper arm b More repair, etc.
Reflex Health- the App for Measuring Shoulder Range of Motion and Tracking Pain
Recovering from an injury can be tough. You’re not sure what exercises to do, how often to do them, or whether you’re making progress.
It’s hard to stay motivated when progress is slow. Feeling like you’re not making any headway can be demotivating and lead to giving up on your recovery altogether.
This can lead to never regaining your full Range of Motion Potential.
Over 70% of people never complete their rehab
The Reflex Health App takes the guesswork out of recovering from an injury. With this app, you can accurately measure your shoulder range of motion in minutes from the comfort of your own home.
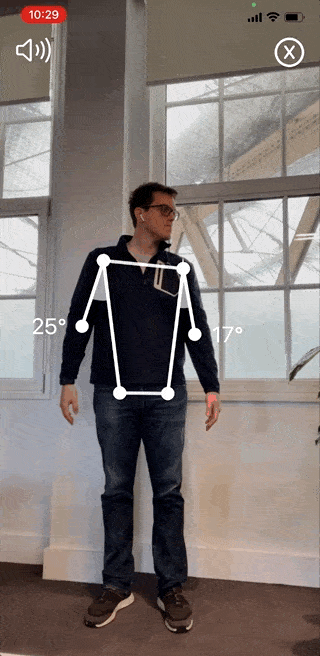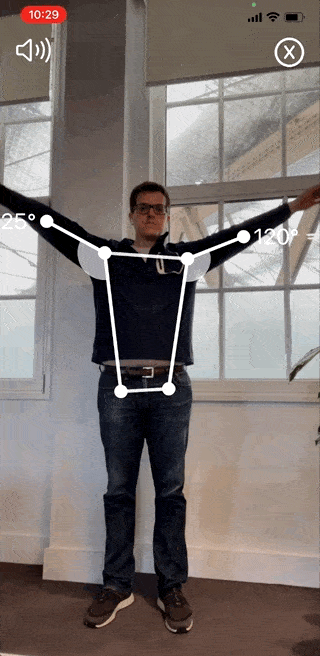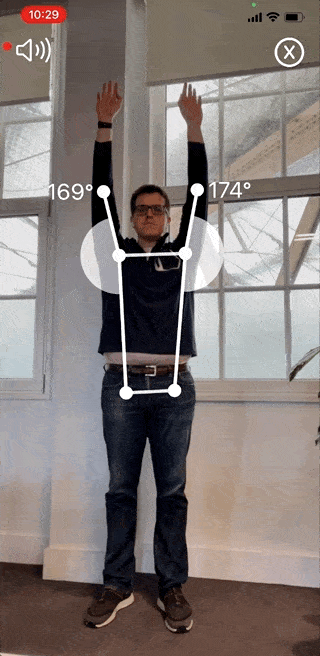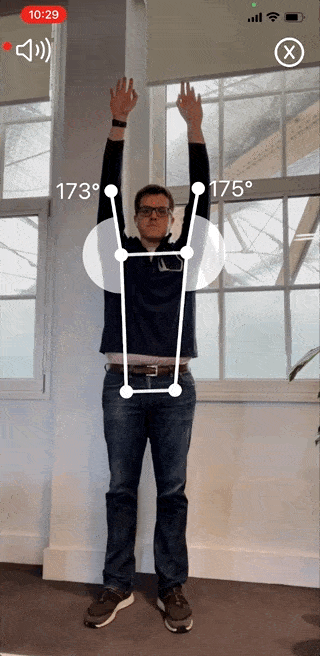
You’ll also be able to track your progress over time and see what exercises are working best for you. This way, you’ll stay motivated throughout your recovery journey, even when progress is slow.
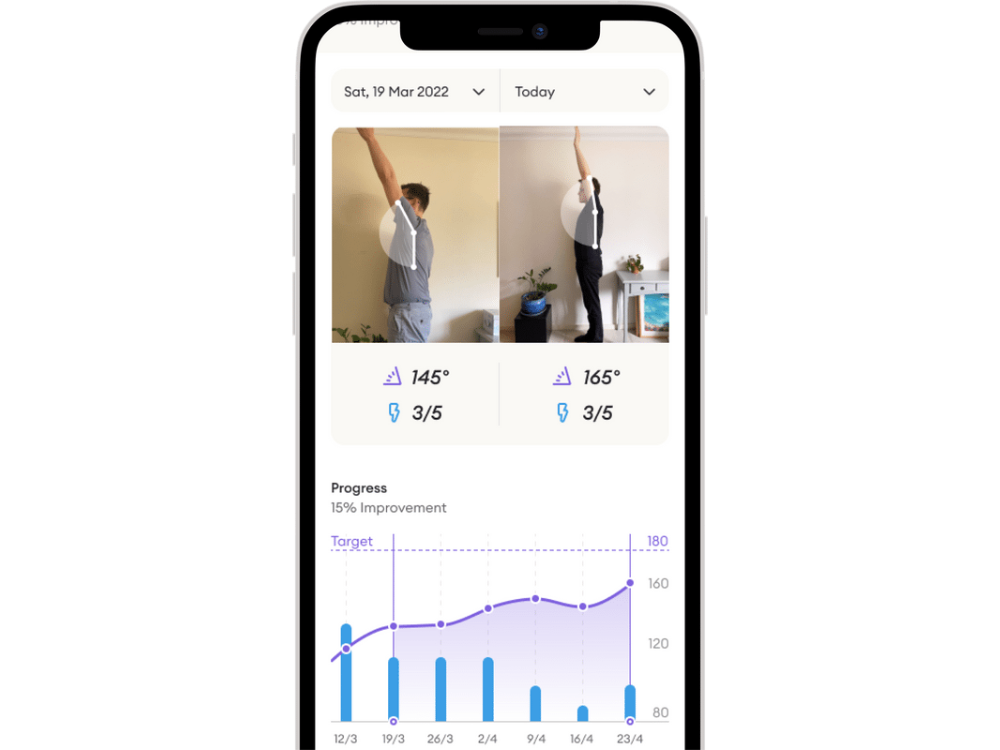
Track pain across all shoulder movements. When your pain reduces, that indicates that you’re ready for the next stage of physiotherapy.